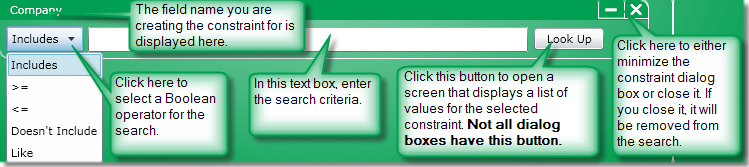
All constraint dialog boxes contain controls that let you specify search criteria. However, the controls available will vary depending on the field name chosen. For example, the Call Type constraint contains check boxes that let you specify as many call types as necessary while the Duration constraint contains a list box where you can specify a Boolean operator and a text box to enter a duration.
With Report Publisher, all constraints are not available for every report. That is, depending on the report chosen, only certain constraints can be used with that report.
The operators available will vary depending on the constraint chosen.
After selecting a constraint from the Add Additional Constraint list box, a dialog box for that constraint will appear. There, you can further define search criteria to narrow the search.
Most of the constraint dialog boxes look like the one shown below. Exceptions will be displayed when you click for more information on a constraint.

Click below to find more information on a constraint that begins with that character or letter:
Click for information on the % Abandoned Calls constraint.
This constraint lets you include only those summary lines containing the percentage of abandoned calls that meet the specified criteria.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for more information on the % of Calls constraint.
This constraint is used to include people in a report whose percentage of calls for a specific device type is at a specified value. For example, if someone selects Hard Phones from the Device Type list box, selects >= from the % of Total Calls list box, and enters 90 in the text box, then only people whose hard phone usage by call count that was greater than or equal to 90% are included in the report.
Note: This constraint will show all of a person's usage, not just the usage for the selected device type.

To use the % of Calls constraint, follow these steps:
From the Device Type list box, select a device.
From the % of Total Calls list box, select an operator. Choices are: Includes, <=, and >=.
In the % of Total Calls text box, enter a value.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Click for more information on the % of Duration constraint.
This filter is used to include people in a report whose percentage of usage by duration for a specific device type is at a specified value. For example, if someone selects Tablet from the Device Type list box, selects <= from the % of Total Calls list box, and enters 75 in the text box, then only people whose tablet usage by duration was less than or equal to 75% are included in the report.
Note: This constraint will show all of a person's usage, not just the usage for the selected device type.

To use the % of Duration constraint, follow these steps:
From the Device Type list box, select a device.
From the % of Total Calls list box, select an operator. Choices are: Includes, <=, and >=.
In the % of Total Calls text box, enter a value.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Abandoned constraint.
The Abandoned constraint controls whether or not abandoned calls are included in the reports.

To use the Abandoned constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
If you do not want abandoned calls as part of the search criteria, click Exclude Abandoned Calls.
If you want all calls as part of the search criteria, click All Calls. This is the default setting.
If you want only abandoned calls as part of the search criteria, click Include Only Abandoned Calls.
The selected option will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Account constraint.
This constraint controls what records appear in your results based on the account code. Some phone systems allow the entry of a code to show for whom the call was made, e.g. a specific client.
With this constraint, you can search by:
A specific code or codes
Codes that fall within certain categories

To search for a specific code or codes, perform the following:
Select the Query specific Account codes option button.
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the code or codes. If entering multiple codes, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for account codes.
After selecting the codes at the Select screen, click OK to save the selections.
The codes will then appear in the Constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.

To search for account codes that fall within certain categories, perform the following:
Select the Or query by option button.
From the list of option buttons, select the one desired for the search.
Your selection will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Area Code constraint.
This constraint lets you include or exclude calls with specific area codes.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Area Code Exchange constraint.
This constraint lets you include or exclude calls with specific area code/exchanges.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Auth Code constraint.
This constraint controls what records appear in your results based on the authorization code. With this constraint, you can search by:
A specific code or codes
Codes that fall within certain categories

To search for a specific code or codes, perform the following:
Select the Query specific authorization codes option button.
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the code or codes. If entering multiple codes, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for account codes.
After selecting the codes at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The codes will then appear in the Constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.

To search for account codes that fall within certain categories, perform the following:
Select the Or query by option button.
From the list of option buttons, select the one desired for the search.
Your selection will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Average Duration constraint.
Using the <= , >=, and Includes operators along with specifying an average duration (in seconds), this constraint lets you include only summary lines where the average duration meets the criteria entered.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Average Ring Time Abandoned
constraint.
This constraint lets you include a specific ring time average, or a ring time average equal to or greater than, or a ring time average equal to or less than a specified ring time before a call is abandoned.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Average Ring Time Answered
constraint.
This constraint lets you include a specific ring time average, or a ring time average equal to or greater than, or a ring time average equal to or less than a specified ring time before a call is answered.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Avg Dur Exception constraint.
This constraint lets you include calls whose average duration for a person, depending on the operator used, exceeds or is less than the specified value. This constraint uses the <= and >= operators.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Average Inbound Duration
Exception constraint.
This constraint lets you include calls whose average duration of inbound calls for a person, depending on the operator used, exceeds or is less than the specified value. This constraint uses the <= and >= operators.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Avg Out Dur Exception constraint.
This constraint lets you include calls whose average duration of outbound calls for a person, depending on the operator used, exceeds or is less than the specified value. This constraint uses the <= and >= operators.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Avg Ring Time Exception
constraint.
This constraint lets you include the average ring time for a person that, depending on the operator used, exceeds or is less than the specified value. This constraint uses the <= and >= operators.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Base Cost constraint.
This is the cost based on the billing class assigned to base cost.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Billable Fee constraint.
This constraint is available when the following conditions are met:
You purchased the PSP option
You activated the Enhanced PSP option by clicking the Use Special PSP Billing check box located on the Enhanced PSP dialog box in System Configuration Options
This constraint will search on individual fees.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Billable Time constraint.
This constraint is available when the following conditions are met:
You purchased the PSP option
You activated the Enhanced PSP option by clicking the Use Special PSP Billing check box located on the Enhanced PSP dialog box in System Configuration Options
This constraint will search on entities that meet the billable time criteria.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Billed Cost constraint.
This constraint searches on the cost based on the billing class assigned to the billing class.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Billing Class constraint.
Owners and account codes can belong to different billing classes. This constraint allows calls over a group of trunks to be billed differently for different people.
This type of constraint dialog box uses a Look Up button that opens a screen where you can search for values appropriate to the selected field name. To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for values specific to the field name chosen.
After selecting the values at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The values will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Billing Pool constraint.
This constraint lets you control which billing pools appear in a report.
Note: Only calls that have been processed as part of a pool will appear in the report.
This type of constraint dialog box uses a Look Up button that opens a screen where you can search for values appropriate to the selected field name. To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for values specific to the field name chosen.
After selecting the values at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The values will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Billing
Pool Reason constraint.
This constraint contains a group of check boxes that let you select the reason or reason a call was priced the way it was included in your search.

To use the Pool Reason constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
Click the check box next to each reason you want included in the search.
The selected reason or reasons will be part of the search criteria.
Click the Clear button to remove all selections from the search criteria.
Click for information on the Call Leg Duration constraint.
This constraint lets you include or exclude call legs based on their duration, and is formatted as HH:MM:SS. If you enter just a “3”, it is assumed you mean 00:00:03 (3 seconds).
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Call Type constraint.
This constraint contains a group of check boxes that let you select the call type or types you want included in your search.

To use the Call Type constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
Click the check box next to each call type you want included in the search.
The selected call type or types will be part of the search criteria.
If you click the Select All button, all choices for that constraint will be selected.
Note: The Select All button provides a more convenient method of selecting all choices except one or two. For example, when all call types except internal are required, click the Select All button and then deselect Internal.
Click the Clear All button to remove all selections from the search criteria.
Click for information on the Call Type INB/INT constraint.
This constraint lets you include inbound calls, internal calls, or both types of calls in the report.

To use the Call Type INB/INT constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
If you want just inbound calls as part of the search criteria, click Inbound Calls Only.
If you want just internal calls as part of the search criteria, click Internal Calls Only.
If you want both types of calls as part of the search criteria, click Include Inbound and Only Internal Calls.
The selected option will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Caller ID constraint.
These are the unformatted digits that show what was received from caller id. May be different than the phone number on a trunk-to-trunk call where caller ID shows the incoming digits and phone number shows the outgoing digits.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Carrier Matched constraint.
Note: The Carrier Matched constraint will be available only if the Call Reconciliation Option is turned on.
This constraint only applies to records eligible for matching. This is due to those records belonging to a carrier data source or to a data source/facility combination that is matched to a carrier.
To use the Carrier Matched constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
If you want just matched and unmatched records as part of the search criteria, click Matched and Unmatched Records. This is the default selection.
If you want just matched records as part of the search criteria, click Matched records Only.
If you want just unmatched records as part of the search criteria, click Unmatched records Only.
The selected option will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Cause Code Type constraint.
This constraint controls which type of cause code is included in the reports.

To use the Cause Code Type constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
If you want all codes as part of the search criteria, click All Codes.
If you want only failure cause codes as part of the search criteria, click Only Failure Cause Codes.
If you want only normal cause codes as part of the search criteria, click Only Normal Cause Codes.
The selected option will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the City constraint.
This constraint will narrow a search by searching a city name
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Conference Cost constraint.
This constraint allows you to include in the report any conference where the conference cost matches the criteria you specify. This filter uses the Includes, <=, and >= operators.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Conference Count constraint.
This constraint allows you to include in the report any conference where the number of participants matches the criteria you specify. This filter uses the Includes, <=, and >= operators.
Note: The organizer is included in the total number of participants.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Conference Duration constraint.
This constraint allows you to include in the report any conference where the conference duration matches the criteria you specify. This filter uses the Includes, <=, and >= operators.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Cost constraint.
This constraint allows you to include or exclude calls based on their cost.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Cost or Duration constraint.
This constraint uses an "or" operator and lets you include records that match either a cost or duration criteria but the record does not have to match both.
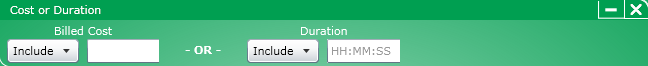
To use the Cost or Duration constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
In the Billed Cost section, perform the following:
Select an operator from the list box. The ">=", and "<=" operators are the only operators available.
In the Billed Cost text box, enter an amount
In the Duration section, perform the following:
Select an operator from the list box. The ">=", and "<=" operators are the only operators available.
In the Duration text box, enter a length of time
Click OK to save the selections.
The selections will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Country Code constraint.
This constraint searches for the country assigned to the facility that recorded the call.
This type of constraint dialog box uses a Look Up button that opens a screen where you can search for values appropriate to the selected field name. To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for values specific to the field name chosen.
After selecting the values at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The values will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Data Source Group Name
constraint.
This constraint is only available if the Networked PBX option is on.
Networked PBX systems have a group level above the data sources that indicates which PBX systems are tied together.
This type of constraint dialog box uses a Look Up button that opens a screen where you can search for values appropriate to the selected field name. To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for values specific to the field name chosen.
After selecting the values at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The values will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Data Source Name constraint.
This constraint searches on the name of the data source that produced the CDR.
This type of constraint dialog box uses a Look Up button that opens a screen where you can search for values appropriate to the selected field name. To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for values specific to the field name chosen.
After selecting the values at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The values will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Destination Cause Code
constraint.
This constraint allows you to choose which codes to include in the report for the receiving participant.

This type of constraint dialog box uses a Look Up button that opens a screen where you can search for values appropriate to the selected field name. To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 1;9.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for values specific to the field name chosen.
After selecting the values at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The values will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Destination Country constraint.
This constraint lets you specify the destination countries in the Combined Calls Summary by Destination Country – City report.
This type of constraint dialog box uses a Look Up button that opens a screen where you can search for values appropriate to the selected field name. To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for values specific to the field name chosen.
After selecting the values at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The values will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Click for more information on the Device Name constraint.
This constraint lets you include (or exclude) a device name or names in the report.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the device name or names. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each.
The values you enter will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Device Type constraint.
This constraint controls which device type will appear or not appear in the report.
With this constraint, you can search by:
A specific device type or types
Device types that fall within certain categories

To search for a specific device type or types, perform the following:
Select the Query specific device types option button.
From the drop-down list box, select an operator. Available operators for this constraint are Includes, Doesn't Include, and Like.
In the text box, enter the device type or types. If entering multiple device types, use a semi-colon to separate each.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Device Type screen where you can search for device types.
After selecting the device types at the Select Device Type screen, click OK to save the selections.
The device types will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Note: If no device types are specified, all device types will be included in the report.
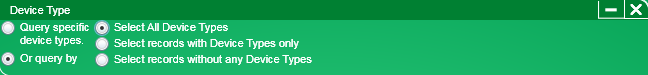
To search for device types that fall within certain categories, perform the following:
Select the Or query by option button.
From the list of option buttons, select the one desired for the search.
Your selection will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Disconnect Initiator constraint.
This constraint contains a group of check boxes that let you select the disconnect initiator you want included in your search.

To use the Disconnect Initiator constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
Click the check box next to each choice you want included in the search.
The selected choices will be part of the search criteria.
If you click the Select All button, all choices for that constraint will be selected.
Note: The Select All button provides a more convenient method of selecting all choices except one or two. For example, when all choices except Transfer are required, click the Select All button and then deselect Transfer.
Click the Clear All button to remove all selections from the search criteria.
Classification of who disconnected (disconnect initiator) choices:
Calls involving external parties (outbound and inbound calls)
PSTN
Inside
Calls where both parties are internal (internal calls)
Inside (P) if it is the person who placed the call.
Inside (R) if it is the person who received the call
For Cisco there are calls where nobody hung up because they are legs of calls that are continued.
Transfer if the call was transferred
Conference if the call became part of a conference
If who hung up cannot be determined the value is Unknown.
If the PBX does not provide the information then the value is Unsupported.
Click for information on the DNIS constraint.
This filter controls what records appear based on the DNIS code.
With this constraint, you can search by:
A specific code or codes
Codes that fall within certain categories

To search for a specific code or codes, perform the following:
Select the Query specific DNIS codes option button.
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the code or codes. If entering multiple codes, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for DNIS codes.
After selecting the codes at the Select screen, click OK to save the selections.
The codes will then appear in the Constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.

To search for DNIS codes that fall within certain categories, perform the following:
Select the Or query by option button.
From the list of option buttons, select the one desired for the search.
Your selection will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the DNIS Code Description constraint.
This constraint searches on the name assigned to the DNIS code in the DNIS database.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the DNIS Code Group constraint.
This constraint searches on the DNIS groups in the DNIS database.
This type of constraint dialog box uses a Look Up button that opens a screen where you can search for values appropriate to the selected field name. To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for values specific to the field name chosen.
After selecting the values at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The values will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Duration constraint.
This constraint lets you include or exclude calls based on their duration, and is formatted as HH:MM:SS. If you enter just a "3", it is assumed you mean 00:00:03 (3 seconds).
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Equal Access constraint.
This constraint lets you to include or exclude calls based on equal access digits used to make the call.
This type of constraint dialog box uses a Look Up button that opens a screen where you can search for values appropriate to the selected field name. To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for values specific to the field name chosen.
After selecting the values at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The values will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Export Date constraint.
This constraint allows you to include or exclude calls based on the date the record was reported to the Time and Billing system.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Extension constraint.
This constraint searches on the reporting extension that either made an outgoing call or received an incoming call.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for more information on the Extension Location
constraint.
This constraint allows you to include or exclude extension locations from the report.
This type of constraint dialog box uses a Look Up button that opens a screen where you can search for values appropriate to the selected field name. To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for values specific to the field name chosen.
After selecting the values at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The values will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Click for more information on the Extension Location Destination constraint.
This constraint allows you to specify which extension location destinations can be included or excluded from the report.
This type of constraint dialog box uses a Look Up button that opens a screen where you can search for values appropriate to the selected field name. To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for values specific to the field name chosen.
After selecting the values at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The values will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Facility Name constraint.
This filter allows you to include or exclude calls based on the facility.
This type of constraint dialog box uses a Look Up button that opens a screen where you can search for values appropriate to the selected field name. To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for values specific to the field name chosen.
After selecting the values at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The values will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Filename constraint.
This constraint lets you include in the report the name of the file that was transferred.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Final Called Party Number constraint.
There are two conditions for the Final Called Party Number constraint:
For forwarded calls, this constraint filters on the last party to receive the call
For non-forwarded calls, this constraint filters on the original called party
Note: Final Called Party Number is a term specific to Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Gateway constraint.
This constraint appears only for QOS reports. It allows you to run the report for just one gateway.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Has Recordings constraint.
The Has Recordings constraint controls whether or not calls with voice and/or video recordings are included in the reports.

To use the Has Recordings constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
If you want all calls as part of the search criteria, click All Calls. This is the default setting.
If you want to include only calls with voice recordings as part of the search criteria, click Calls with Voice Recordings.
If you want to include only calls with video recordings as part of the search criteria, click Calls with Video Recordings.
If you want to include only calls with both voice and video recordings as part of the search criteria, click Calls with Either Voice or Video Recordings.
If you want to include only calls with no recordings as part of the search criteria, click Calls with No Recordings.
The selected option will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Home Site constraint.
A home site is the physical location to which an owner belongs. This constraint searches on the home site.
This type of constraint dialog box uses a Look Up button that opens a screen where you can search for values appropriate to the selected field name. To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for values specific to the field name chosen.
After selecting the values at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The values will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Hunt Group Name constraint.

This constraint lets you include or exclude calls based on the name of the selected hunt group.
This type of constraint dialog box uses a Look Up button that opens a screen where you can search for values appropriate to the selected field name. To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for values specific to the field name chosen.
After selecting the values at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The values will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Hunt Group Number constraint.

This constraint lets you include or exclude calls based on the selected hunt group number.
This type of constraint dialog box uses a Look Up button that opens a screen where you can search for values appropriate to the selected field name. To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for values specific to the field name chosen.
After selecting the values at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The values will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Inter-Location Calls constraint.
The Inter-Location Calls constraint controls whether or not internal calls made to the same location or between locations are included in the reports.
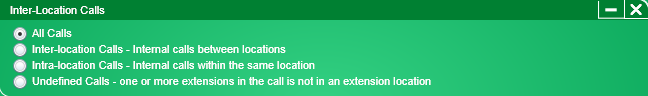
To use the Inter-Location Calls constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
If you want all calls as part of the search criteria, click All Calls. This is the default setting.
If you want to include only calls made between locations as part of the search criteria, click Inter-Location Calls.
If you want to include only calls made within the same location as part of the search criteria, click Intra-Location Calls.
If you want to include only calls that have one or more extensions not in an extension location as part of the search criteria, click Undefined Calls.
The selected option will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Initiating Extension constraint.
This constraint will limit the contents of the report to the specified extension(s) that initiated the transferred call.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Initiator constraint.
This constraint will include the person who brought each participant into the conference call.
This type of constraint dialog box uses a Look Up button that opens a screen where you can search for values appropriate to the selected field name. To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for values specific to the field name chosen.
After selecting the values at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The values will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Is Conf. Call constraint.
The Is Conf. Call constraint controls whether or not conference calls are included in the reports.

To use the Is Conf. Call constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
If you want all calls as part of the search criteria, click All Calls. This is the default setting.
If you want only conference calls as part of the search criteria, click Only Conference Calls.
If you do not want conference calls as part of the search criteria, click Exclude Conference Calls.
The selected option will be part of the search criteria.
Click for more information on the Jitter constraint.
This constraint is used only for QOS reports and is the variation in latency of VoIP calls.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for more information on the Jurisdiction constraint.
This constraint lets you select call types within a country you select.

To use the Call Type constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the Country list box, select a country.
A group of call type check boxes for the selected country will appear.
If you click the Select All button, all choices for that constraint will be selected.
Note: The Select All button provides a more convenient method of selecting all choices except one or two. For example, when all call types except Local are required, click the Select All button and then deselect Local.
Click the Clear All button to remove all selections from the search criteria.
Click for information on the Latency constraint.
This constraint is used only for QOS reports and is a measure of the time it takes for a packet of data to be assembled and travel from its source to destination.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Local Base Cost constraint.
This is the cost based on the billing class assigned to the local base cost.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Local Billed Cost constraint.
This constraint searches on the local cost based on the billing class assigned to the billing class.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Local Profit constraint.
This constraint lets your search on the difference between the local billed and local base cost.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Matching Arena constraint.
This constraint lets you specify matched arenas.
This type of constraint dialog box uses a Look Up button that opens a screen where you can search for values appropriate to the selected field name. To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for values specific to the field name chosen.
After selecting the values at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The values will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Matter Codes constraint.
This constraint is used in conjunction with account codes and allows calls to be broken not only into groups of who the matter codes were created for, but into sub-groups within that group.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Media Type constraint.
This constraint contains a group of check boxes that let you select the media type or types you want included in your search.

To use the Media Type constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
Click the check box next to each media type you want included in the search.
The selected media type or types will be part of the search criteria.
Click the Clear button to remove all selections from the search criteria.
Click for information on the Message Count constraint.
This constraint will include the number of messages made by each participant whose total messages are more than/equal to or less than/equal to what is specified.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Mobility Call constraint.
This constraint lets you choose if calls that use the mobility feature are included in the report.

To use the Mobility Call constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
If you want all types of calls as part of the search criteria, click All Calls.
If you want only calls that use the mobility feature as part of the search criteria, click Show Only Calls That Use the Mobility Feature.
If you want to exclude calls that use the mobility feature from the search criteria, click Exclude Calls That Use the Mobility Feature.
The selected option will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Nbr of Calls Exception
constraint.
This constraint lets you include the number of calls for a person that, depending on the operator used, exceeds or is less than the specified value. This constraint applies to all calls and uses the <= and >= operators.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Nbr Inb Calls Abandoned
Except constraint.
This constraint lets you include the number of abandoned inbound calls for a person that, depending on the operator used, exceeds or is less than the specified value. This constraint uses the <= and >= operators.
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Nbr Int Calls Abandoned
Except constraint.
This constraint lets you include the number of abandoned internal calls for a person that, depending on the operator used, exceeds or is less than the specified value. This constraint uses the <= and >= operators.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Nbr of Inb Calls Exception
constraint.
This constraint lets you include the number of inbound calls for a person that, depending on the operator used, exceeds or is less than the specified value. This constraint uses the <= and >= operators.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Nbr of Int Calls Exception
constraint.
This constraint lets you include the number of internal calls for a person that, depending on the operator used, exceeds or is less than the specified value. This constraint uses the <= and >= operators.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Nbr of Out Calls Exception
constraint.
This constraint lets you include the number of outbound calls for a person that, depending on the operator used, exceeds or is less than the specified value. This constraint uses the <= and >= operators.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Nbr Trans Calls Initiated
constraint.
This constraint will limit the report to transferred calls where the organizational level initiated the number of specified transferred calls.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Nbr Trans Calls Participated
constraint.
This constraint will limit the report to transferred calls where the organizational level participated in the number of specified transferred calls.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Nbr Trans Calls Terminated
constraint.
This constraint will limit the report to transferred calls where the organizational level terminated the number of specified transferred calls.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for more information on the Networked Calls constraint.
A networked call is one that originated on one PBX, was transferred over a tie line to another PBX, and went out to the public phone system on the second PBX.

To use the Networked Calls constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
If you want all calls as part of the search criteria, click All Calls.
If you want only networked calls as part of the search criteria, click Only Networked Calls.
If you do not networked calls as part of the search criteria, click Exclude Networked Calls.
The selected option will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Node constraint.
This constraint is used only for QOS reports. It allows the user to run the report on just one node of the voice network.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Number of Call Legs constraint.
This constraint will have the report display the specified number of call legs.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for more information on the Operator Assisted
constraint.
This constraint controls what records appear based on if the call is operator assisted.

To use the Operator Assisted constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
If you want all calls as part of the search criteria, click All Calls.
If you want only operator assisted calls as part of the search criteria, click Only Operator-Assisted Calls.
If you do not operator assisted calls as part of the search criteria, click Exclude Operator-Assisted Calls.
The selected option will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Organization Levels constraint.
This constraint searches for the organization level in the Directory database. The organization level names were defined at installation.
This type of constraint dialog box uses a Look Up button that opens a screen where you can search for values appropriate to the selected field name. To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for values specific to the field name chosen.
After selecting the values at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The values will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Organizer constraint.
This constraint lets you include only those conference calls where the person you specify is the organizer.
This type of constraint dialog box uses a Look Up button that opens a screen where you can search for values appropriate to the selected field name. To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for values specific to the field name chosen.
After selecting the values at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The values will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Original Called Party Number
constraint.
This constraint will filter on the phone number that was originally called and after any digit translations have occurred.
Note: Original Called Party Number is a term specific to Cisco Unified Communications Manager.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Originating Cause Code
constraint.
This constraint allows you to choose which codes to include in the report for the participant making the call.

This type of constraint dialog box uses a Look Up button that opens a screen where you can search for values appropriate to the selected field name. To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 1;6.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for values specific to the field name chosen.
After selecting the values at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The values will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Originating Data Source
Name constraint.
This constraint searches for the data source that originated a networked call.
This type of constraint dialog box uses a Look Up button that opens a screen where you can search for values appropriate to the selected field name. To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for values specific to the field name chosen.
After selecting the values at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The values will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Owner constraint.
This constraint searches for the person who originated the instant message transaction.
This type of constraint dialog box uses a Look Up button that opens a screen where you can search for values appropriate to the selected field name. To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for values specific to the field name chosen.
After selecting the values at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The values will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Owner Name constraint.
This constraint searches for the user to whom the call is assigned.
This type of constraint dialog box uses a Look Up button that opens a screen where you can search for values appropriate to the selected field name. To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for values specific to the field name chosen.
After selecting the values at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The values will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Packets Lost constraint.
This constraint is used for QOS reports only and it lets you search on how many packets were lost in the transmission of a call.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Participant constraint.
This constraint lets you include the people you specify that were participants in a conference call.
This type of constraint dialog box uses a Look Up button that opens a screen where you can search for values appropriate to the selected field name. To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for values specific to the field name chosen.
After selecting the values at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The values will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Participant Count constraint.
This constraint is used to look for any conference where the participant count matches the criteria you specify.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Participating Extension
constraint.
This constraint will limit the contents of the report to transferred calls where the specified extension is included in at least one of the call legs.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Pct Packets Lost constraint.
This constraint is used for QOS reports only and it lets you search on the percentage of how many packets were lost in the transmission of a call.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Phone Group Name constraint.
This constraint is based on the groups in the Phone Number database.
This type of constraint dialog box uses a Look Up button that opens a screen where you can search for values appropriate to the selected field name. To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for values specific to the field name chosen.
After selecting the values at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The values will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Phone Name constraint.
This constraint is based on the names assigned to numbers in the Phone Number database.
This type of constraint dialog box uses a Look Up button that opens a screen where you can search for values appropriate to the selected field name. To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for values specific to the field name chosen.
After selecting the values at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The values will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Phone Number constraint.
This constraint allows you to search for calls with a specific digits dialed pattern.
Note: You must include the leading 1 for long distance or 011.
This type of constraint dialog box uses a Look Up button that opens a screen where you can search for values appropriate to the selected field name. To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for values specific to the field name chosen.
After selecting the values at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The values will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Profit constraint.
This constraint lets your search on the difference between the billed and base cost.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Queued Calls constraint.
This constraint allows you to choose whether calls that were waiting to be routed and then answered to be included or excluded from a report.

To use the Queued Calls constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
If you want all calls as part of the search criteria, click All Calls.
If you want to include only queued calls click the Include only Queued Calls control.
If you want to exclude exclude queued calls click the Exclude Queued Calls control.
The selected option will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Queue Time constraint.
This constraint indicates the time taken before calls were routed and then answered.

To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator. Choices are: Includes, <=, =>.
In the text box, enter the value (in seconds). For example, 10.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria (in seconds).
Click for information on the Raw Extension constraint.
This constraint lets you search on the actual extension that either made an outgoing call or received an incoming call.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Receiver Name constraint.
This constraint lets you include in the report the name of the people that received the transferred file.
This type of constraint dialog box uses a Look Up button that opens a screen where you can search for values appropriate to the selected field name. To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for values specific to the field name chosen.
After selecting the values at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The values will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Redirected Calls constraint.
This constraint lets you either to include or exclude redirected calls in a report.

Note: This constraint will only be made available when VoIP is enabled.
To use this dialog box, follow these steps:
If you want all calls as part of the search criteria, click All Calls.
If you choose the only redirected calls option you will include only calls where Original Called Party Number is not equal to the Final Called Party Number.
If you choose the exclude redirected calls option you will include only calls where Original Called Party Number is equal to the Final Called Party Number.
The selected option will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Responder constraint.
This constraint lets you include the people that were chosen as responders of the instant message.
This type of constraint dialog box uses a Look Up button that opens a screen where you can search for values appropriate to the selected field name. To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for values specific to the field name chosen.
After selecting the values at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The values will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Ring Time constraint.
This constraint lets you include a specific ring time, or a ring time equal to or greater than, or a ring time equal to or less than a specified ring time before a call is answered in the report.
This constraint lets you include a specific ring time, or a ring time equal to or greater than, or a ring time equal to or less than a specified ring time before a call is answered in the report.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Ring Time Service Level
constraint.
This filter uses an "and" operator. Using this filter lets you search for records that are either greater than or equal to or less than or equal to a specified service level goal and a percentage specified answered ring time.
For each of these values, you can specify an operator (<=, >=, or Includes). Entering the values along with their operators, you can filter only those calls that were answered a specified percentage of the time in a specified amount of time. For example, if the first value is >=80 (Service Level Goal) and the second value is <=30 (Ring Time), the result will be that only summary lines where the person/dept/etc. answered at least 80% of the calls in less than or equal to 30 seconds will appear.

To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
In the Service Level Goal section, perform the following:
Select an operator from the list box. The ">=", and "<=" operators are the only operators available.
In the Value text box enter a service level goal in a percentage
In the Ring Time section, perform the following:
Select an operator from the list box. The ">=", and "<=" operators are the only operators available.
In the Value text box enter a ring time in seconds
Click OK to save the selections.
The selections will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Sender constraint.
This constraint lets you include in the report the name of the person that sent the transferred file.
This type of constraint dialog box uses a Look Up button that opens a screen where you can search for values appropriate to the selected field name. To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for values specific to the field name chosen.
After selecting the values at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The values will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Source Facility Name constraint.
On a trunk-to-trunk call, this is the facility to which the originating trunk belongs.
This type of constraint dialog box uses a Look Up button that opens a screen where you can search for values appropriate to the selected field name. To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for values specific to the field name chosen.
After selecting the values at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The values will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Source Trunk Group constraint.
On a trunk-to-trunk call, this is the trunk group to which the originating trunk belongs.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Source Trunk Member constraint.
On a trunk-to-trunk call, this is the originating trunk.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the State Name constraint.
Use this constraint to narrow a search by specifying a state name.
This type of constraint dialog box uses a Look Up button that opens a screen where you can search for values appropriate to the selected field name. To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
Alternatively, click the Look Up button to open a Select Value screen where you can search for values specific to the field name chosen.
After selecting the values at the Select Value screen, click OK to save the selections.
The values will then appear in the constraint dialog box text box and will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Status constraint.
This constraint lets you include the status of the file transfer in the report. Click each status type to include it in the report. Choices include:
Accepted
Rejected
Canceled
Error
Note: By default, none of the options are selected.
Click for more information on the Summary Billable Fee constraint.
This constraint is available when the following conditions are met:
You purchased the PSP option
You activated the Enhanced PSP option by clicking the Use Special PSP Billing check box located on the Enhanced PSP dialog box in System Configuration Options
This constraint will search on total billable fees for line item. For example, total billable fees for a person.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Summary Cost constraint.
This constraint will include only those extensions whose total cost is more than or equal to or less than or equal to what is specified.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Summary Count constraint.
This constraint will include only those extensions whose total calls are more than or equal to or less than or equal to what is specified.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Summary Cost Duration or
Count constraint.
The Summary Cost Duration or Count constraint uses an "or" operator that lets you search for records that match either a cost, a count, or a duration. The resultant records do not have to match all three.
Note: The "Includes", ">=", and "<=" operators are the only operators available for this type of constraint.
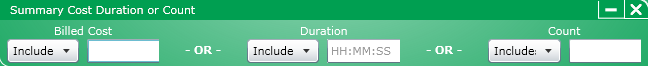
To use this constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
In the Billed Cost section select an operator and in the text box enter an amount.
In the Duration section select an operator and in the text box enter a length of time.
Tip: The Duration text box indicates how the search criteria are to be formatted.
In the Count section select an operator and in the text box enter a number.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Summary Duration constraint.
This constraint will include only those extensions whose total call length is more than or equal to or less than or equal to what is specified.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Summary PTD Billable Fee constraint.
This constraint is available when the following conditions are met:
You purchased the PSP option
You activated the Enhanced PSP option by clicking the Use Special PSP Billing check box located on the Enhanced PSP dialog box in System Configuration Options
This constraint will search on billable fees for the date range chosen at the Required Constraints tab.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click
for information on the Summary PTD Billable Fee constraint.
This constraint is available when the following conditions are met:
You purchased the PSP option
You activated the Enhanced PSP option by clicking the Use Special PSP Billing check box located on the Enhanced PSP dialog box in System Configuration Options
This constraint will search on the billable hours for the date range chosen at the Required Constraints tab.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click
for information on the Summary PTD Billable Fee constraint.
This constraint is available when the following conditions are met:
You purchased the PSP option
You activated the Enhanced PSP option by clicking the Use Special PSP Billing check box located on the Enhanced PSP dialog box in System Configuration Options
This constraint will search on billable fees for the year to date (the current date back to January 1st of the current year).
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Summary PTD Billable Hours constraint.
This constraint is available when the following conditions are met:
You purchased the PSP option
You activated the Enhanced PSP option by clicking the Use Special PSP Billing check box located on the Enhanced PSP dialog box in System Configuration Options
This constraint will search on billable hours for the year to date (the current date back to January 1st of the current year).
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Tandem Calls constraint.
Note: The Tandem Calls constraint will be available only if the Call Reconciliation Option is turned on.
This constraint lets you indicate how you want to handle the Tandem calls.
To use the Tandem Calls constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
If you want to include just original calls and exclude combined calls in the search criteria, click Include Original Calls, Exclude Combined Calls. This is the default selection.
If you want to include just combined calls and exclude original calls in the search criteria, click Include Combined Calls, Exclude Original Calls.
If you want to include both original and combined calls in the search criteria, click Include Original and Combined Calls.
The selected option will be part of the search criteria.
Click for information on the Terminating Extension constraint.
This constraint will limit the contents of the report to the specified extension(s) that terminated the transferred call.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Tot Cost Exception constraint.
This constraint lets you include the total cost of calls for a person that, depending on the operator used, exceeds or is less than the specified value. This constraint uses the <= and >= operators.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Tot Inb Dur Exception constraint.
This constraint lets you include calls whose total duration of inbound calls for a person, depending on the operator used, exceeds or is less than the specified value. This constraint uses the <= and >= operators.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Tot Int Dur Exception constraint.
This constraint lets you include calls whose total duration of internal calls for a person, depending on the operator used, exceeds or is less than the specified value. This constraint uses the <= and >= operators.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Tot Out Dur Exception constraint.
This constraint lets you include calls whose total duration of outbound calls for a person, depending on the operator used, exceeds or is less than the specified value. This constraint uses the <= and >= operators.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Total Call Duration constraint.
This constraint lets you include or exclude call legs based on the total length of the call, and is formatted as HH:MM:SS. If you enter just a “3”, it is assumed you mean 00:00:03 (3 seconds).
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Total Calls constraint.
This constraint uses the following operators: <=, >=, and Includes. After selecting an operator and specifying the total number of calls, only summary lines that meet the criteria will appear in the report.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Total Duration Exception
constraint.
This constraint lets you include calls whose total duration for a person, depending on the operator used, exceeds or is less than the specified value. This filter applies to all calls and uses the <= and >= operators.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Trunk Group constraint.
With this constraint, you can narrow a search by specifying a trunk group.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Trunk Member constraint.
With this constraint, you can narrow a search by specifying a trunk member.
To use this type of constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
From the drop-down list box, select an operator.
In the text box, enter the value or values. If entering multiple values, use a semi-colon to separate each, and a hyphen to indicate a range. For example, 7117;7119;7121-7131.
The values you enter will be a part of the search criteria.
Tip: The text box in some constraint dialog boxes indicate how the search criteria are to be formatted.
Click for information on the Trunk to
Trunk constraint.
This constraint controls whether or not trunk to trunk calls are included in the reports.

To use the Trunk to Trunk constraint dialog box, follow these steps:
If you want all calls as part of the search criteria, click All Calls. This is the default setting.
If you want only trunk to trunk calls as part of the search criteria, click Only Trunk to Trunk Calls.
If you do not want trunk to trunk calls as part of the search criteria, click Exclude Trunk to Trunk Calls.
The selected option will be part of the search criteria.